Accounts payable and accounts receivable (AP-AR) automation is at the core of creating real-time visibility into a business’ working capital. With an estimated market value of USD 3.52 billion by 2030[1], it is also at the heart of the fintech innovation that is disrupting the traditional treasury services market. API-led AP-AR automation solutions today connect a business’ treasury, payments and credit workflows, creating unprecedented access for digital first players in the payments and lending space.
The shift from AP-AR automation to a holistic business finance management solution is more notable in SaaS-based providers targeting niche small and medium enterprises (SMEs) that are born digital-first, or have shown marked digital adoption over the past half decade. The broadening of AP-AR automation solutions typically covers financial automation capabilities like automated book-keeping and reconciliation, e-invoicing automation, embedded payments, short-term revolving credit and point of sale lending.
According to an Accenture study[2] banks are still the preferred treasury management service providers, but 44% customers have considered moving to a fintech provider for lower costs, ease of use and ease of integration. This poses a serious unbundling risk to banks’ commercial and corporate banking business, which accounts for over USD 2.7 trillion in global banking revenues[3].
In this blog, we cover the broadening landscape of AP-AR automation led solutions, and look at how adopting these solutions can help banks seed engagement and business results across the SME business banking workflow.
The changing landscape of AP-AR automation solutions
The global AP-AR automation market size was valued at USD 1.9 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 3.52 billion by 2030. It consists of key incumbent players and challengers (who are more agile in the APAC region).
Of late, focus has shifted to monetising B2B payments and lending, especially SME business’ share of the same. Global B2B payments flows are expected to exceed USD 200 trillion by 2028[4]. The global commercial lending market is expected to yield USD 27 trillion in revenues between 2021 and 2028, with SMEs accounting for USD 13 trillion of these revenues[5].
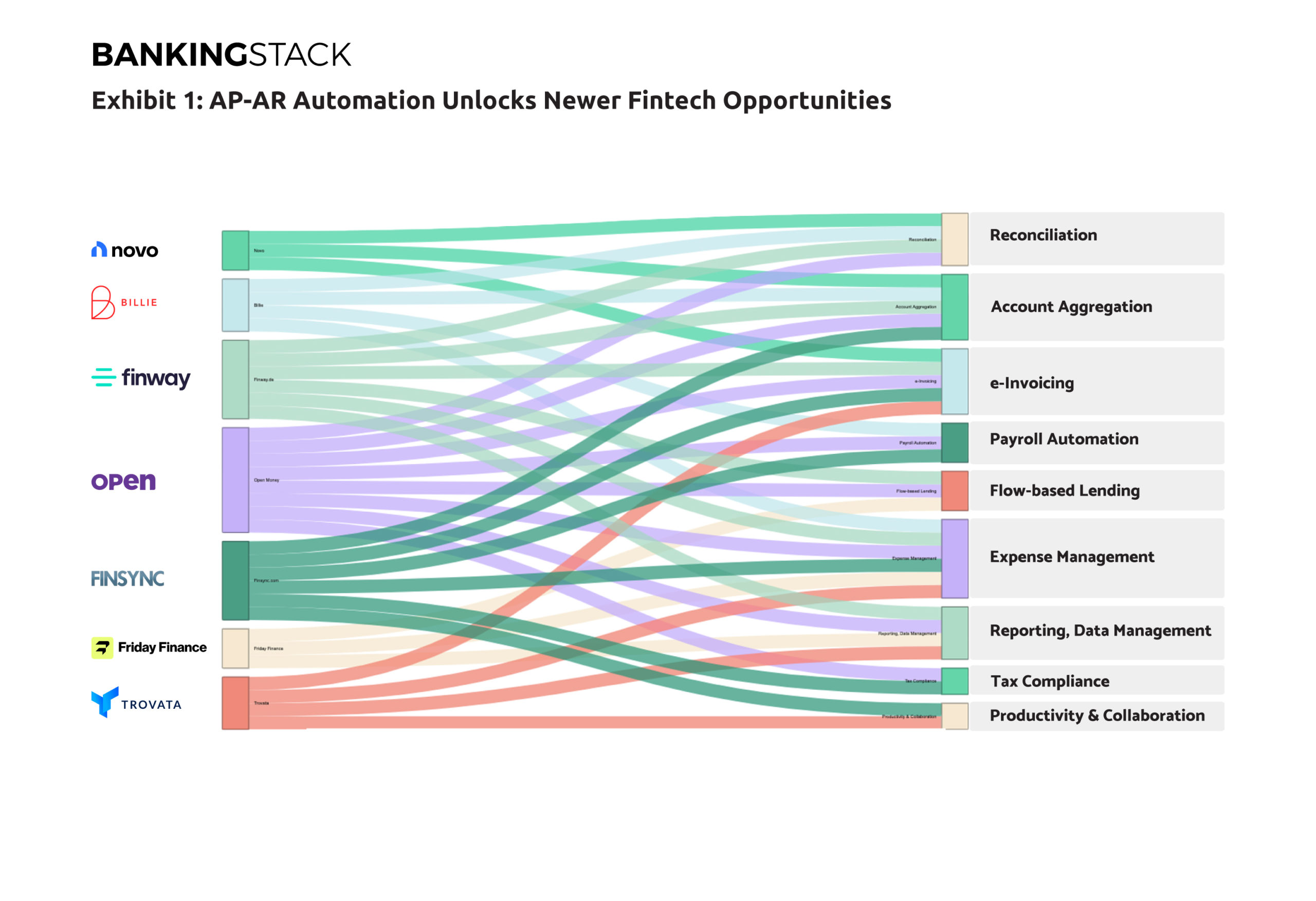
For AP-AR automation solution providers therefore, moving towards integrating AP-AR automation with payments and credit capabilities has emerged as the next logical step. Exhibit 1 illustrates how several fintechs have successfully developed end to end business finance management platforms for MSMEs, including payments, alternative lending, and supply chain finance, with AP-AR automation at the core.
Small merchants further benefit from partnerships among banks, FIs and fintech players, as well as from big players adding SME relevant features in their products. For example:
- Double-entry book keeping and bank reconciliation have been added as new features to FreshBooks Accounting software.
- American Express is creating an end-to-end B2B platform by building capabilities and partnerships with BillTrust and Versapay.
- Singapore based IFS capital, a provider of customised financing solutions in Southeast Asia, partners with global B2B payments player PrimeRevenue to offer digital payments and AP automation, integrating seamlessly with ERP solutions. The partnership brings supply chain finance to companies across Southeast Asia[6].
- DBS Singapore offers a collection solution to SMEs called DBS MAX, delivering automated AP and AR features to its merchant clients. It has entered into a partnership with Dairy Farm Singapore for a supplier financing programme.
AP-AR automation can drive SME engagement across banking products
The story of how AP-AR automation led solutions are moving to unbundle traditional business banking solutions is one of many similar fintech-led plays. What’s common is the ability to keep the SME merchant engaged within one seamless ecosystem, with value-added services and traditional banking products offered in a contextual, integrated manner.
With banks, the challenge in countering such plays remains their siloed business structures. While several leading banks have already made moves to embed their payments and lending products within digital ecosystems, this is largely a distribution play, and is usually restricted to a specific product or business line. Moreover, it does not deliver the same extent of access to or engagement with the businesses.
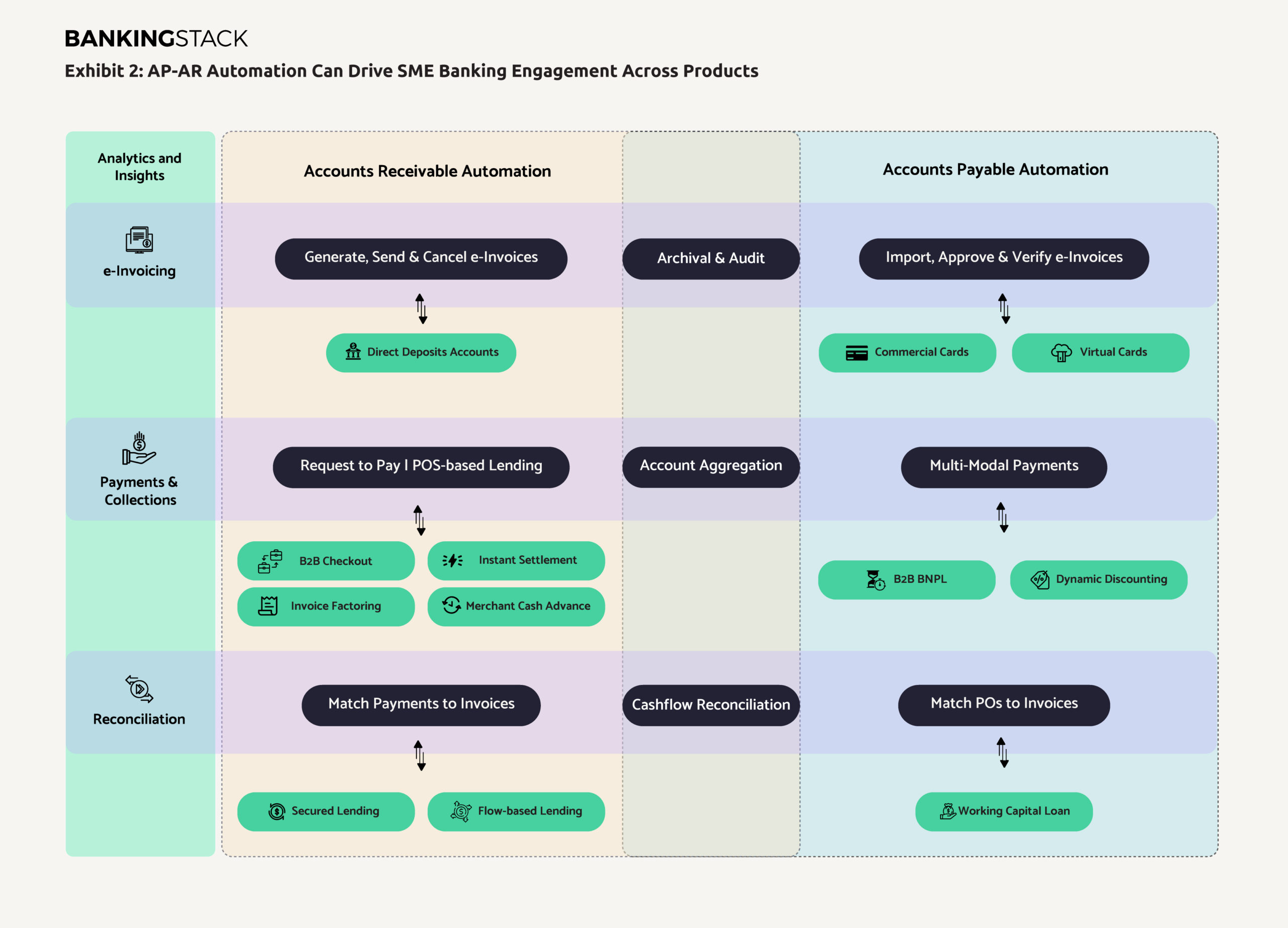
Partnering with SaaS-based providers, who can use banking APIs to deliver a seamless flow between business banking and beyond banking capabilities (like AP-AR automation, B2B payments and point of sale lending) can help banks overcome this challenge. Exhibit 2 illustrates the seeding of banking products across a business’ AP-AR automation workflow, supported by the following financial automation capabilities:
- e-Invoicing: Automation around government-mandated e-Invoicing has fuelled use cases like real-time continuous transaction controls and clearance, with suppliers and buyers exchanging invoices via centralised government infrastructure. Importantly, automation around government validated e-invoices, integrated with banking and payment services can enable highly value-adding capabilities like invoice approval and scheduling, recurring payments, and purchase returns.
The data from these streams also plays an important role in selection and agreement of terms of supply chain finance solutions like reverse factoring and dynamic discounting at the point of sale. - Payments: B2B payments facilitation is emerging as a key value pool in commercial banking. McKinsey estimates that banks earned over USD 1 trillion in revenues from commercial payments alone[7]. The ability to embed payments within the AP-AR automation flow is pushing fintech innovation towards a cohesive ‘B2B checkout’ experience, clubbing together multiple payment modes, credit options and reconciliation capabilities.
Payment fintechs have made steady progress in this direction, using transactional data and alternative risk-assessment to deliver transaction or PoS-based lending to SMEs. - Account aggregation: Fintechs are riding on the open banking framework to give businesses visibility across bank accounts. This has unlocked access to advanced cash flow forecasting capabilities for SMEs, while giving the offering bank current insights into the business’ financial flows.
- Reconciliation: Matching of payments and invoices across B2B payments is challenging, and automatic matching capabilities are only available on supplier portals offered by a few banks and financial institutions to corporate customers. Financial automation can help SMEs eliminate 80% workload and reduce payment errors by over 50%[8].
Importantly, automated reconciliation is helping drive the digital origination, underwriting and agreement workflows of supply chain finance offerings.
Conclusion
McKinsey estimates that customer ownership, with an ‘ecosystem experience’ where customers can access multiple services seamlessly is one of the top three reasons for a bank’s outperformance in the digital economy[9]. Business focused banks that have managed to deliver this to their customers have achieved over 70% premiums in their valuations when compared to universal banks[10].
The unbundling of commercial banking services through AP-AR automation calls for a similar strategy in delivering end-to-end business finance management, with built-in levers for engagement and ownership.
Note: This article was originally published on Finextra Community Blogs here: https://www.finextra.com/blogposting/23750/ap-ar-automation-can-unlock-sme-engagement-for-banks
[1] Verified Market Research; AP-AR Automation Market Size, Share, Trends and Opportunities; https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/ap-ar-automation-market/
[2] Accenture; Banks to Grow their Treasury Management Business; https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insightsnew/banking/what-banks-do-grow-treasury-management-business#accordion-e74faaef20-item-80c5b2e9b4
[3] McKinsey; Global Banking Annual Review; https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/financial-services/our-insights/global-banking-annual-review
[4] Goldman Sachs; B2B: How the next payments frontier will unleash small business; https://www.gspublishing.com/content/research/en/reports/2019/09/04/201b4777-6217-4638-9701-fb98d67d9d5d.pdf
[5] Research Dive; https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2022/04/25/2428250/0/en/Global-Commercial-Lending-Market-Anticipated-to-Generate-a-Revenue-of-27-406-6-Billion-and-Rise-at-a-CAGR-of-14-4-during-the-Forecast-Timeframe-from-2021-to-2028-190-Pages-Reveals-.html
[6] SGX Announcement; https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5f34fa182e4f8d02498cf62b/t/632085beb3b6d9180747dd81/1663075775800/SGX+Announcement__Update+on+the+Non-Binding+MOU+in+relation+to+Strategic+Partnership+with+PrimeRevenue+Inc.pdf
[7] McKinsey; Global Payments Report 2022; https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/industries/financial%20services/our%20insights/the%202022%20mckinsey%20global%20payments%20report/the-2022-mckinsey-global-payments-report.pdf
[8] AvidXchange; Breaking Down the Cost Saving Benefits of AP Automation; https://www.avidxchange.com/blog/cost-saving-benefits-ap-automation-solutions-breakdown/
[9] McKinsey; Global Banking Annual Review 2021; https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/industries/financial%20services/our%20insights/global%20banking%20annual%20review%202021%20the%20great%20divergence/global-banking-annual-review-2021-the-great-divergence-final.pdf
[10] McKinsey; Global Banking Annual Review 2022; https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/financial-services/our-insights/global-banking-annual-review